Commonly asked interview questions for Instrumentation Engineers
Commonly asked interview questions for Instrumentation Engineers
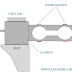
What are different types of orifice plates? State their uses.
Different orifice plates are: 1. Concentric 2. Segmental 3. Eccentric
- Concentric: These plates are used for ideal liquid as well as gases and steam service. Concentric holes are present in these plates, thats why it is known as concentric orifice.
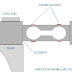
- Segmental: This plate has hole in the form of segment of the circle. This plate is used for colloidal and sherry flow measurement.
- Eccentric: This plate has the eccentric holes. This plate is used in viscous and sherry flow measurement.
How do you identify an orifice in the pipeline?
An orifice tab is welded on the orifice plate which extends out of the line giving an indication of the orifice plate.
Why is the orifice tab provided?
Following reasons justify for providing orifice tab:
1. Indication of orifice plate in a line
2. The orifice diameter is marked on it.
3. The material of the orifice plate.
4. The tag number of the orifice plate.
5. To mark the inlet of an orifice.
Explain Bernoulli’s theorem. State its application.
Bernoulli’s theorem states that the ‘total energy of a liquid flowing from one point to another remains constant’. It is applicable for non-compressible liquids. For different types of liquid flow Bernoulli’s equation changes. There is direct proportion between speed of fluid and its dynamic pressure and its kinetic energy. It can be used in various real life situations like measuring pressure on aircraft wing and calibrating the airspeed indicator. It can also be used to low pressure in the venturi tubes present in carburetor.
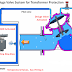
How can a D.P. transmitter be calibrated?
D.P. transmitter can be calibrated using following steps:
1. Adjust zero of Xmtrs.
2. Perform static pressure test: Give equal pressure on both sides of transmitter. Zero should not shift either side. If the zero shifts then carry out static alignment.
3. Perform vacuum test: Apply equal vacuum to both the sides. Zero should not shift.
4. Calibration procedure: Give 20 psi air supply to the transmitter and vent L.P. side to atmosphere. Connect output of the instrument to the standard test gauge. Adjust zero. Apply required pressure to the high pressure side and adjust the span. Adjust zero gain if necessary.
How is flow measured in square root?
Flow varies directly as the square root of pressure. Thus, F=K of square root of applied pressure. Since this flow varies as the square root of differential pressure. The pressure pen does not directly indicate flow. Thus flow can be determined by taking the square root of the pen. Assume the pen reads 50% of the chart. So, flow can be calculated using the pen measure in the chart.
Name different parts of a pressure gauge. Explain the use of hair spring in the pressure gauge.
Pressure gauge includes following components:
a. ‘C’ type bourdon tube.
b. Connecting link
c. Sector gear
d. Pinion Gear
e. Hair spring
f. Pointer
g. Dial
Use of hair spring: Hair spring is responsible for controlling torque. It is also used to eliminate any play into linkages.
How D.P. transmitter can be applied to close tank?
In closed tank, bottom of the tank is connected to the high pressure side of the transmitter. Top of tank is connected to the lower pressure side of the transmitter. In this way vessel pressure can be measured.
How D.P. transmitter can be applied to open tank?
In open tank the lower pressure side is vented to the atmosphere. All pressure is applied to the high pressure side. This vessel pressure is measured through high pressure side.
Explain the working of an electronic level troll.
The variation in level of buoyancy resulting from a change in liquid level varies the net weight of the displacer increasing or decreasing the load on the torque arm. This change is directly proportional to change in level and specific gravity of the liquid. The resulting torque tube movement varies the angular motion of the rotor in RVDT providing a rotor change proportional to the rotor displacement, which is converted and amplified to a D.C. current.
Explain the working of an enraf level gauge.
Enraf level gauge is based on the ser powered null balance technique. A displacer serves as continuous level sensing element. A two phase ser motor controlled by a capacitive balance system winds unwinds the the measuring wire until the tension in the weight springs is in balance with the weight of the displaced part immersed in the liquid. The sensing system in balance measures the two capacitance formed by the moving central sensing rod provided by the two capacitor plates and the si plates.
What is the constant voltage unit?
The constant voltage circuit consists of a rectifier, CR and a filter capacitor. It is followed by two stages of zener regulation. Abridge configuration is provided to lamp line voltage zener regulation. Regulation 1 and regulation 2 provides relatively provide constant current. Resistors form a bridge that may remoment line voltage effects.
Explain the burnout feature.
Burnout provides the warnsug feature of driving indicator at the end of scale, if the input circuit is open. A burnout resistor is provided which develops a voltage drop between the measuring circuit and amplifier. The polarity of the signal determines the direction of the servo drive upon an open circuit in the input.
Upscale burnout: R value 10 M
Downscale burnout: R value 22 M
Why thermo wells are used? What materials are used in thermo wells?
In numerous applications, it is neither desirable nor practical to expose a temperature sensor directly to a material. Wells are therefore used to protect against damage corresion, arosion, aborsion and high pressure processes. A thermo well is also useful in protecting a sensor from physical damage during handling and normal operations.
Materials used in thermo wells: Stainless steel, Inconel, Monel, Alloy Steel, Hastelloy














Leave a Comment